It is a well known fact that when
the body gets some cut the blood starts oozing from the
wound. the force with which the blood will come out of the
body will depend on the blood pressure of the body and
location of the effected part with respect to the location
of the heart. In any case the force of out coming blood will
be just near to blood pressure of the body.
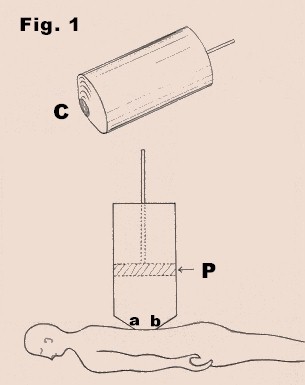
In Fig. 1, let a b is the portion
of the body where a cut is formed and the blood is oozing
out of the cut. A pump with piston P is placed on the
exposed location of the body. The pump is placed in such a
way that its open mouth C covers the wounded portion. Now,
if the piston is moved upward it will create some vacuum
over the wound and the blood will start coming out more
violently. Again, if the piston P is moved downward
gradually, the pressure over the wound will start increasing
and the blooding will start decreasing. The blood will stop
leaking out at a critical pressure over the wound. In
this way a blood free field can be prepared at any exposed
portion of the body.
The blood pressure within the
heart will be a little more than the blood pressure observed
by the sphygmometer. Similarly, the blood pressure will be
different at different parts of a body depending on the
distance of that part from the heart.
Now, if the pump is enlarged in
such a way that the surgeons can also enter the area of
critical pressure, they can perform surgery in a blood free
field.
If any part of the body is cut
opened in a space having pressure just equal to the sum of
atmospheric pressure and blood pressure of that part of the
body, while keeping rest of the body in atmospheric pressure
with opened part upward, there will be no bleeding from the
exposed portion.
Or, in order to stop bleeding the
difference of two pressures, the one in which the body is
kept and the other in which any part of the body is cut
opened, should be just equal to the blood pressure of that
part of the body.
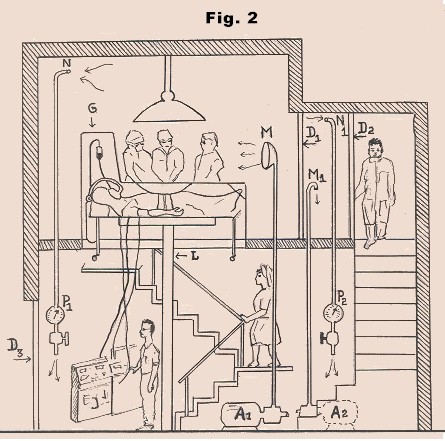
In Fig. 2, the doctors and the
exposed part of the patient is placed in a space having
pressure equal to the sum of atmospheric pressure and blood
pressure of the exposed part of the patient while the
patient is lying under normal atmospheric pressure.
The normal blood pressure of a
human body goes to about 150 mm of mercury i.e., equal to
200 milibars of atmospheric pressure. The average
atmospheric pressure, which is about 1000 millibars at the
sea level, goes on decreasing as we go higher and higher.
The annual mean pressure at Darjiling, which is about 7432
feet from the sea level, is about 775 milibars. It shows the
man can live in such a variable pressures. Therefore, the
addition of blood pressure in the atmospheric pressure will
not harm the surgeons working in it.
Ground floor is the control room
and first floor is operation room. The two are separated by
a glass cabin G. D3
is the entrance for control room and D2
is the entrance for operation room. The operation room is
having two air tight doors D1
and D2. A1
and A2 are two air pumps. Pump A1
pushes the air in the operation room from inlet M.
The only exit for air from operation room is from N.
A desirable pressure is maintained in the operation room by
controlling the out going air from P1.
In order to make it possible for
surgeons to move in and out of the operation room without
disturbing the pressure in the room, two air tight doors D1
and D2 are provided. The
pressure between D1 and
D2 is kept equal to the pressure of the operation
room by a air pump A2 and
outlet P2.
During exit from operation room
the doctor will open the door D1
and enter the space between D1
and D2. He will open the door D2
after closing the door D1.
During entrance in the operation
room the doctor will enter from door D2
and open the door D1 after
allowing the pressure between D1
and D2 to reach the pressure of
the operation room. A pressure gauge is attached at door D1
( not shown in Fig. ) to help doctor, standing in between D1
and D2 to see the pressure
difference between the operation room and the space of D1
and D2. The complete system can
be automated by computer technology, The computers will be
able to control all pressures by directly sensing the blood
pressure of the patient and the atmospheric pressure. The
computers will also lock and unlock doors after sensing
different pressures.
The patient is brought in the
glass cabin G by lifting him
from the control room by the L.
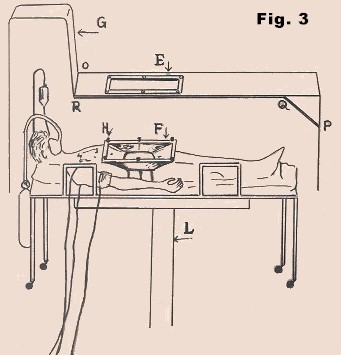
In Fig. 3, E
is the open part of the glass cabin G.
F is a funnel type arrangement
made up of rubber. The upper edge of the funnel F
is attached to rectangular metallic frame and the lower edge
is tied with the patient.
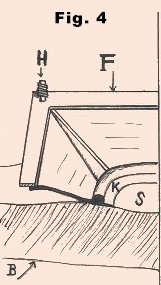
Fig. 4, shows cross-section of
the funnel F with its lower
edge in contact with the body. The lower edge of the funnel
is designed in such a way to make it leakage proof for air
under pressure. The compressed air will press the thin leaf K
with the skin making the contact air tight. Before attaching
the funnel F with the body,
some thick oil is applied at the place of its contact with
the body to make it completely air-tight. The upper edge of
the funnel F is brought in
contact with the frame E by net
bolts and the contact is made air tight. B
is the body of the patient and S
is the portion of the body to be operated.
The design of the glass cabin G,
funnel F and resting position
of the patient will be unique for different type of
operations. During the surgery of the brain, the best
position of the patient will be vertical. The complete
patient will be clamped with soft pads to hold him
vertically.
To make the process more
effective the atmosphere of the operation room is to be
controlled by those gases which will prevent clotting of the
blood. The design of the system will be a little different
as each surgeon will have their own breathing masks to
protect chemical composition of the gases and humidity of
the operation room. Their breathing masks will receive and expel
air through special tubes that will be connected to special
system outside the operation room. The pressure of the
operation room will be made to fluctuate slightly in harmony
with heart beat of the patient, so that the pressure will be
always exactly equal to the exposed portion. The complete
system will be controlled by electronic devices.
In this way the surgery can be
further refined. The surgeons will get sufficient time to
operate some delicate parts like brain without extra risk to
the patient. It will also help real time study of the
working of deeper regions of the brain by letting scientists
watch open regions of the brain for a longer period.
In the end I suggest that we
should give a try to this procedure even if it is a little better form the existing system. Some people have died
during surgery just because they could not wait a few
minutes more due to the loss of their precious blood.

We
could have saved them
|
Wednesday,
July 9, 2003 -Singapore:
Neurosurgeons separated the 29-year old Iranian
twins born joined at the head, after two days of
delicate surgery, but both sisters died Tuesday,
shortly after their parting. Laden Bijani died 90
minutes ahead of her sister Lelah with both death occurring
because of blood loss, said hospital officials. |
|
Let
no more such deaths. |




